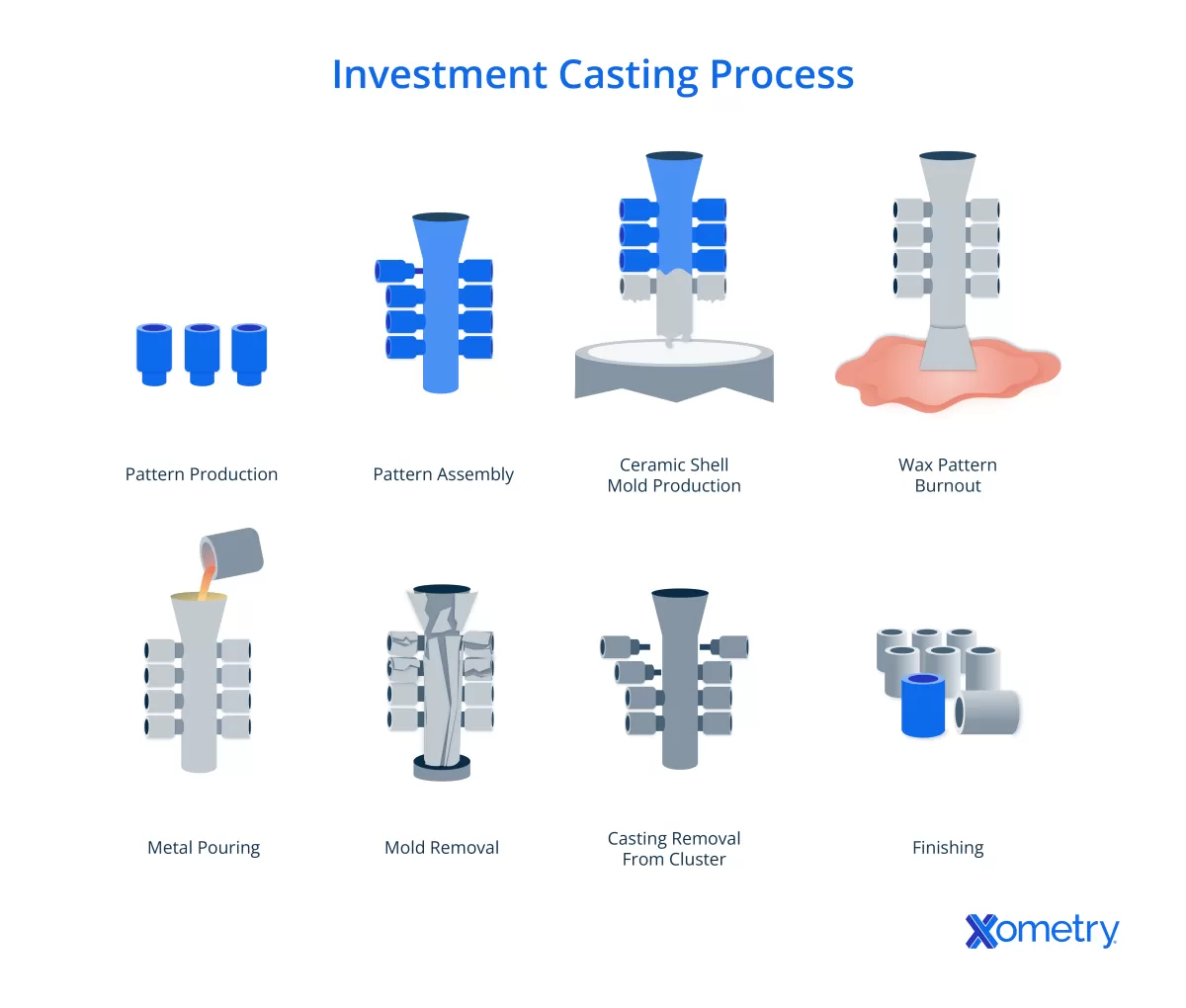
What Is Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, is a precise metal casting process where a wax pattern is coated with a ceramic material to create a mold. Once the ceramic hardens, the wax is melted away, leaving a detailed cavity that can be filled with molten metal. This technique allows for the creation of highly detailed and complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with other casting methods.
Key Features
- High precision and accuracy for intricate designs
- Ability to produce complex geometries and thin walls
- Results in an excellent surface finish that usually requires minimal machining
Common Materials
Investment casting supports a wide range of metals, including:
- Ferrous metals: stainless steel, carbon steel
- Non-ferrous metals: aluminum alloys, copper alloys
Applications
This method is ideal for producing:
- Aerospace components
- Medical devices
- Intricate parts for the automotive industry
HYCNC’s Role
At HYCNC, we specialize in precision CNC machining to improve and refine investment cast parts. This means tighter tolerances, better fits, and superior finishes—perfect for clients who need reliable, high-quality components that meet strict specifications.
What Is Die Casting

Die casting is a metal casting process where molten metal is injected at high pressure into reusable metal molds, also called dies. This method uses durable steel molds that can be used repeatedly, making it ideal for fast, high-volume production.
Key Features
- Fast production cycles
- Cost-effective for large runs
- Good dimensional accuracy out of the mold
Common Materials
- Non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium
Typical Applications
- Automotive housings
- Consumer electronics parts
- Large-scale components
HYCNC’s Role
HYCNC provides precision secondary CNC machining for die cast parts, helping achieve tighter tolerances and better surface finishes. This ensures your parts meet the demanding standards required for specialized industries and helps enhance overall part quality.
Key Differences Between Investment Casting and Die Casting
Process Comparison
Investment casting uses disposable wax and ceramic molds, making it a multi-step and labor-intensive process. Die casting, on the other hand, relies on reusable metal molds with high-pressure injection, which is mostly automated and much faster.
Material Flexibility
Investment casting works with both ferrous metals like stainless and carbon steel and non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper alloys. Die casting is usually limited to non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium due to the high temperatures of metal molds.
Design Complexity
Investment casting shines when making intricate shapes, thin walls, and detailed features. Die casting is better suited for simpler designs and larger parts that don’t require fine detail.
Production Volume
If you’re making a small to medium batch—from about 10 to 10,000 pieces—investment casting is a strong choice. For high-volume production, into the thousands or millions, die casting is more cost-effective.
Surface Finish and Tolerances
Investment casting offers superior surface finish (around 125 micro-inch Ra) and tighter tolerances (typically IT5-6), which often means less machining after casting. Die cast parts usually have a good surface finish but may need secondary CNC machining to meet tight tolerance requirements.
Cost Considerations
Investment casting comes with a higher per-unit cost but lower tooling expenses since molds are disposable. Die casting has higher upfront tooling costs for reusable molds but delivers a lower cost per part when producing large volumes.
Each method has clear advantages depending on your project’s size, design complexity, and budget. Understanding these key differences will help you pick the right casting process.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Investment Casting Pros and Cons
Pros:
- High precision with excellent detail and surface finish
- Works with a wide range of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals
- Often needs minimal machining after casting, saving time on finishing
Cons:
- Slower process compared to die casting, not ideal for very high volumes
- Higher cost per part when producing large quantities
- Size limitations, typically up to around 100kg per part
Die Casting Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Fast production speeds, perfect for large volume runs
- Cost-effective when making thousands or millions of parts
- Produces strong, durable parts with good dimensional accuracy
Cons:
- Limited to non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium due to mold temperature limits
- High upfront tooling costs because molds are reusable and made from metal
- Less design flexibility, better suited for simpler shapes rather than intricate details
When to Choose Investment Casting vs Die Casting
Choose Investment Casting if you need:
- Complex, intricate designs or thin-walled parts
- Working with ferrous metals like stainless steel or niche alloys
- Small to medium production runs (10 to 10,000 pieces)
- High precision and excellent surface finish
Example: HYCNC helps aerospace clients manufacture precision turbine blades using investment casting for those tight specs and detailed shapes.
Choose Die Casting if you need:
- High volume production with consistent quality (thousands to millions of parts)
- Non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium
- Larger parts with simpler geometries
- Cost-effective solution for mass production
Example: HYCNC supports automotive clients producing engine housings and consumer electronics parts via die casting, where speed and volume are key.
Quick Guide to Pick the Right Casting Method
| Factor | Investment Casting | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Design Complexity | Intricate, thin walls, detailed | Simple shapes, thicker walls |
| Material Flexibility | Ferrous & non-ferrous alloys | Mostly non-ferrous metals |
| Production Volume | Low to medium runs | High volume production |
| Surface Finish | Superior, minimal machining | Good but often needs machining |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher per unit for large runs | Lower per unit with high volumes |
At HYCNC, we help you decide which method fits your project best, so you get the right balance of precision, cost, and speed.
How HYCNC Enhances Your Casting Project
At HYCNC, we specialize in precision CNC machining that takes your investment casting and die casting parts to the next level. Our expertise helps refine cast components to meet tight tolerances and improve surface finish, ensuring your parts perform exactly as needed.
We offer custom machining solutions tailored to both investment casting and die casting projects. Whether you need intricate detail work on a complex aerospace component or secondary machining for a die cast automotive housing, we have the right tools and experience to deliver quality results quickly and reliably.
For example, we worked with an aerospace client to optimize their investment casting turbine blades. By applying precise CNC machining, we improved dimensional accuracy and surface consistency, directly enhancing the final product’s performance.
Ready to get started? Contact HYCNC for expert advice and fast, tailored quotes through our online platform, and let us help you bring your casting project to perfection.
Learn more about our metal casting services and how we support die casting with secondary machining here.
FAQs
What materials can be used in investment casting vs die casting?
Investment casting works with both ferrous metals like stainless steel and carbon steel, as well as non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper alloys. Die casting is mostly limited to non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium because of mold temperature limits.
Which casting method is more cost effective for small runs?
For small to medium production runs, investment casting is generally more cost effective due to lower tooling costs and its ability to handle complex designs without expensive molds. Die casting usually requires high upfront tooling costs, making it better suited for large volume runs.
Can HYCNC handle secondary machining for cast parts?
Yes, HYCNC specializes in precision CNC machining as a secondary process for both investment casting and die casting parts. This ensures tighter tolerances and a better surface finish to meet exact project specifications.
How long does each casting process take?
Investment casting involves multiple steps like making ceramic molds and wax melting, so it takes longer—typically days to weeks depending on complexity. Die casting is faster, using reusable metal molds and high-pressure injection, with cycle times measured in seconds or minutes for each part.
What industries benefit most from each casting method?
Investment casting fits industries needing intricate, high-precision parts like aerospace, medical devices, and custom automotive components. Die casting is popular in automotive, consumer electronics, and large-scale production sectors where speed and cost efficiency for simpler designs matter most.