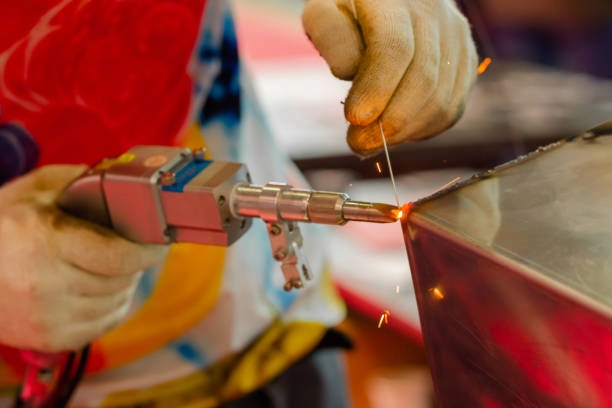
What Are Lasers and How Do They Work
Lasers are devices that produce a focused, intense beam of light. Unlike regular light, laser light is coherent, meaning the light waves match up perfectly, creating a precise and powerful beam. This focused light can cut, engrave, or mark materials with incredible accuracy.
In precision industries like CNC machining, lasers play a key role. They allow for clean cuts, detailed engravings, and efficient welding on metals and plastics. That precision helps manufacturers reduce waste and improve product quality.
Understanding different laser types is essential because each type has unique strengths. Picking the right laser ensures better results, higher efficiency, and cost savings. Whether you’re cutting sheet metal or engraving fine details, knowing which laser fits your needs makes all the difference.
The 10 Most Common Types of Lasers
Gas Lasers (CO2 Lasers)
Gas lasers like CO2 lasers are popular for cutting and engraving non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and leather. They produce a strong infrared beam ideal for precise, clean cuts. At HYCNC, CO2 lasers are a go-to for sheet metal fabrication tasks where high accuracy and smooth edges are essential. They balance power and affordability well, making them a staple in many CNC laser cutting setups.
Solid-State Lasers (Nd:YAG Lasers)
Solid-state lasers use a crystal as the gain medium. Nd:YAG lasers work well for metal marking, welding, and small-scale cutting. They offer high peak power and are great when you need fine details. At HYCNC, these lasers help us handle tougher materials and deliver precision machining with reliable repeatability.
Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are the latest trend in industrial laser tech. They’re energy-efficient, have a long lifespan, and excel at cutting and engraving metals like steel and aluminum. HYCNC uses fiber lasers to boost speed and reduce maintenance downtime. Their high beam quality means less material waste and sharper results, especially important for complex CNC designs.
Semiconductor Lasers (Diode Lasers)
Diode lasers are compact and versatile, often found in lower-power applications such as barcode scanners or pointers. In CNC, they serve niche roles like marking plastics and thin metals. HYCNC leverages diode lasers for quick customization jobs where smaller, cost-effective setups suffice.
Dye Lasers
Dye lasers use liquid organic dyes and can produce tunable wavelengths, useful in research and specialized medical fields. These lasers are less common in typical CNC fabrication but useful at HYCNC for experimental applications where precise wavelength control helps achieve unique material effects.
Excimer Lasers
Excimer lasers emit ultraviolet light, which makes them perfect for delicate surface treatments and micro-machining. While not generally used in large-scale CNC cutting, HYCNC utilizes excimer lasers for high-precision tasks requiring minimal heat impact, like semiconductor manufacturing.
Ruby Lasers
Ruby lasers use synthetic ruby crystals to produce a deep red light. Historically important, they’re now less common but effective in engraving and tattoo removal. HYCNC keeps ruby lasers as a specialty option for materials that respond best to their specific wavelength.
Helium-Neon Lasers
HeNe lasers offer visible red light and are known for stable beam quality. They’re mostly for alignment, measuring, or low-power engraving rather than heavy cutting. At HYCNC, they assist in machine setup and quality control, ensuring everything lines up perfectly before production runs.
Argon-Ion Lasers
Argon-ion lasers emit blue-green light and are used in scientific research, medical treatments, and some engraving processes. In CNC, their high precision is useful for fine engraving on metals and plastics. HYCNC applies argon-ion lasers for specialty custom jobs requiring vivid detail and surface finish.
Chemical Lasers
Chemical lasers generate energy from chemical reactions and produce high-powered beams. Though more common in military or aerospace, they can cut thick materials with ease. HYCNC explores chemical laser tech for future large-scale cutting projects where extreme power is needed, though currently they’re less common in everyday CNC work.
At HYCNC, understanding the strengths of each laser type helps us tailor solutions to your materials and precision needs, making sure you get the best outcome for every project.
How to Choose the Right Laser for Your CNC Needs
Picking the right laser for your CNC projects depends on a few key factors:
-
Material Type
Different lasers work better with different materials. For example, CO2 lasers are great for cutting wood, acrylic, and fabric, while fiber lasers are better for metals like stainless steel and aluminum.
-
Precision Required
Your project’s level of detail matters. If you need super fine engraving, semiconductor or solid-state lasers might be the way to go. For bulk cutting, gas lasers like CO2 can be more efficient.
-
Budget
Laser systems vary widely in cost. Make sure to balance upfront investment with operating costs like maintenance and power consumption.
At HYCNC, we leverage advanced laser technologies tailored to your needs, ensuring you get the most precise cuts and best efficiency at a competitive price. Our experts guide you through this to pick the right laser type that matches your material, job complexity, and budget.
Here’s a quick comparison table to help you see which laser fits your application, power needs, and cost:
| Laser Type | Best for Material | Power Range | Approximate Cost | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Gas Laser | Wood, Acrylic, Leather | Medium to High | Moderate | Cutting, Engraving |
| Fiber Laser | Metals, Plastics | Medium to High | Higher | Metal cutting, Marking |
| Solid-State Laser | Metals, Ceramics | Medium | Moderate to High | Welding, Precision Engraving |
| Semiconductor Laser | Low power tasks, Sensors | Low | Low | Marking, Small-scale Engraving |
| Dye Laser | Specialty Materials | Variable | High | Research, Medical |
| Excimer Laser | Microfabrication | Medium | Very High | Electronics, Micro-machining |
| Ruby Laser | Crystal and Specialty Work | Low to Medium | Moderate | Experimental, Jewelry |
| Helium-Neon Laser | Alignment, Measuring | Low | Low | Positioning, Inspection |
| Argon-Ion Laser | Medical, Scientific | Medium | High | Dermatology, Lab Work |
| Chemical Laser | High power industrial use | Very High | Very High | Military, Aerospace |
Choosing the right laser ensures you get the perfect balance between precision, speed, and cost, especially when working with HYCNC’s expert CNC laser cutting and machining services.
Benefits of Using Lasers in CNC Processing
Lasers bring major benefits to CNC machining, making them a go-to choice for manufacturers in the U.S. Here’s why lasers matter:
Precision and Accuracy
Lasers deliver incredibly precise cuts, engravings, and welds, with minimal material distortion. Whether you’re working on detailed designs or complex shapes, laser technology ensures every edge is sharp and clean. This level of accuracy boosts product quality and reduces waste.
Efficiency and Speed
Laser CNC machines operate fast—much faster than traditional cutting and welding tools. They can handle high-volume production without sacrificing accuracy. This speed means shorter lead times and lower costs, which is a game-changer for competitive industries.
Versatility Across Materials
Lasers work well on a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, wood, and composites. Whether you’re cutting stainless steel, engraving wood panels, or welding thin aluminum, laser CNC machines adapt easily to different tasks, making them incredibly flexible.
HYCNC Services Maximizing Laser Benefits
At HYCNC, we leverage advanced laser technology to offer tailored solutions that meet your specific manufacturing needs. Our expertise helps you choose the right laser type and settings for your project, ensuring the best results on time and on budget. We focus on precision machining and efficient delivery to support your success.
For more tips on laser processing methods, check out our guide on common laser processing methods.