How Laser Cutting Works and Why Material Matters
Laser cutting uses a focused beam of light to precisely cut or engrave materials. Different types of lasers—CO2, fiber, and diode—work best with specific materials because each laser produces different wavelengths and power levels.
- CO2 lasers are great for cutting non-metal materials like wood, acrylic, paper, and leather.
- Fiber lasers excel at cutting metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Diode lasers are often used for engraving and lighter cutting tasks on thin materials.
Several material properties affect how well laser cutting works:
- Thickness: Thicker materials need more power or multiple passes.
- Reflectivity: Shiny metals can reflect the laser beam, making cutting harder or unsafe without a fiber laser.
- Thermal conductivity: Materials that dissipate heat quickly, like aluminum, require more energy to cut.
- Chemical composition: Some materials release harmful gases or melt during laser cutting, demanding extra caution.
Matching the right material to the appropriate laser type ensures clean cuts, safety, and efficiency. This is why understanding both your materials and your laser is key to successful laser cutting.
Materials That Can Be Cut with Laser Cutting
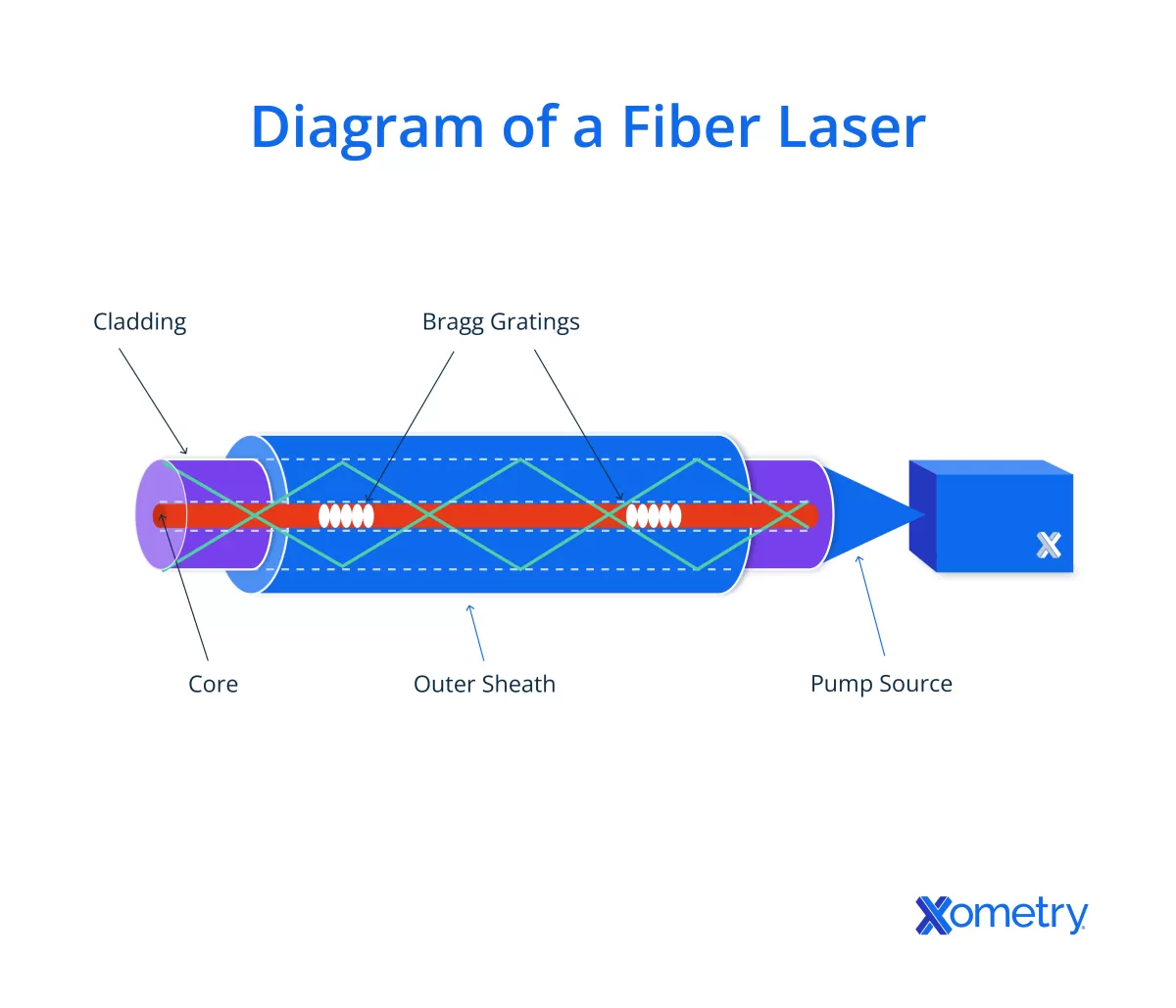
Laser cutting works well with a variety of materials, but knowing which ones are safe and suitable helps you get the best results.
Wood and Wood-Based Materials
Common types like plywood, MDF, balsa, birch, and walnut are great for laser cutting. They cut cleanly and are popular for signs, decorative pieces, and prototypes.
- Tips: Avoid very thick wood to prevent burning or charring. Use lower power settings on softer woods like balsa.
- Caution: Some plywood contains glues or chemicals that may release fumes.
Metals
Laser cutting metals usually requires fiber lasers. Stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and brass are frequently cut materials. Fiber lasers offer high precision on metals with reflective surfaces.
- Tips: Aluminum and brass reflect more light, so make sure your laser system supports these. Stainless steel cuts well with moderate power and slow speeds.
- Caution: Thick metals need more powerful lasers and often gas assist for clean cuts.
Plastics
Acrylic, POM (Delrin), and polyester are good plastic choices for laser cutting. Acrylic in particular is popular for display cases and signage due to its clean edges and smooth finish.
- Tips: Use proper ventilation to avoid fumes. Cut at moderate speeds to prevent melting or scorching.
- Caution: Avoid plastics that release toxic fumes (see next section).
Paper and Cardboard
These materials cut quickly and cleanly with low power settings, making them ideal for packaging, prototyping, and decorations.
- Tips: Adjust power to avoid burning edges, and test different speeds to find the right balance.
Leather and Fabrics
Vegetable-tanned leather cuts well and is often used in fashion and upholstery. Natural fabrics like cotton or polyester work too.
- Tips: Use moderate power and speed to avoid scorching.
- Caution: Some leather treatments and synthetic fabrics may release harmful fumes—always check before cutting.
Foam and Rubber
Thin polystyrene foams and silicone rubber can be cut with controlled settings. These materials are common in packaging and custom padding.
- Tips: Use lower power to avoid melting and deformation. Test samples first for best results.
By selecting the right materials and settings, you’ll get clean, safe cuts and protect your equipment and workspace.
Materials That Cannot Be Cut with Laser Cutting
Certain materials should be avoided with laser cutting due to safety risks and damage potential:
-
PVC and Vinyl
These release toxic chlorine gas when cut, which can corrode your machine and cause serious health hazards. It’s best to choose safer alternatives like acrylic or PET.
-
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate absorbs infrared laser light poorly, leading to discoloration, burning, and fire risks. Instead, use acrylic for clear plastic cutting.
-
ABS
Cutting ABS can release cyanide fumes and cause melting issues. For safety, opt for laser-friendly plastics like POM or polyester.
-
Fiberglass
This material produces harmful fumes and can damage laser equipment. Safer alternatives include wood composites or certain plastics.
-
HDPE and Polypropylene
These plastics often melt, ignite, or leave tough residues when laser cut, making them tricky to handle. Mechanical cutting or routing is recommended.
-
Coated or Galvanized Metals
Zinc coatings on galvanized steel can emit toxic fumes under laser heat. When possible, strip coatings before cutting or choose bare metals.
-
Flame Retardant Materials
Those containing bromine or other flame retardants can give off dangerous gases. Always verify materials and avoid cutting without proper ventilation and safety measures.
Avoiding these materials not only keeps your workspace safe but protects your laser cutter from damage. Always check the material’s chemical makeup and safety info before cutting.
Safety Tips for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is powerful but can be dangerous without the right safety measures. Here’s what I recommend to keep your workspace safe:
-
Use proper ventilation and fume extraction systems
Laser cutting releases fumes and particles, some of which can be toxic depending on the material. Good airflow and extraction help keep the air clean and protect your health.
-
Wear protective gear
Always use laser safety goggles designed for your laser type. Respirators are also a smart choice, especially when cutting plastics or coated materials that release harmful gases.
-
Check Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
Before cutting any material, review its MSDS to understand any health risks or special handling instructions. This helps avoid unexpected toxic fumes or reactions.
-
Match laser settings to your material
Adjust power, speed, and wavelength according to the material type and thickness. Using incorrect settings can cause fires, excessive smoke, or poor cuts.
At HYCNC, we prioritize safe, high-quality CNC processing. Our expert team ensures every job follows strict safety protocols and uses advanced equipment designed for precision and user protection. Your safety is always part of our process.
Choosing the Right Laser Cutter for Your Materials
Picking the right laser cutter depends a lot on the materials you want to work with. CO2 lasers are great for cutting non-metal materials like wood, acrylic, paper, and leather. Fiber lasers, on the other hand, are the go-to for metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass because they offer sharper precision and faster cutting speeds.
At HYCNC, we use advanced laser cutting machines that match the laser type perfectly to your material. This helps us deliver clean cuts and reduces waste while keeping safety a top priority.
When choosing a laser cutter, consider these key factors:
- Bed Size: Make sure the cutting area fits your material piece size.
- Cutting Speed: Faster speeds improve efficiency but might affect edge quality.
- Cooling Systems: Proper cooling keeps the laser running smoothly and prevents overheating, especially during long projects.
- Power Settings: Adjustable power lets you handle a range of materials without damaging them.
By matching your material to the right laser cutter and settings, you get better results, less downtime, and safer operation. HYCNC’s expertise ensures you get the right setup for your project every time.
Common Applications of Laser Cutting by Material
Laser cutting is super versatile and used across many industries. Here’s a quick look at common uses based on material types:
Wood
- Signage: custom store signs, nameplates
- Furniture: intricate designs on tables, chairs
- Decorative art: wall hangings, detailed carvings
Metal
- Automotive parts: brackets, panels
- Aerospace components: lightweight, precise metal parts
- Tools and machinery pieces
Acrylic
- Displays: retail stands, product showcases
- Lighting fixtures: decorative lamps, LED covers
Paper and Cardboard
- Packaging: custom boxes, inserts
- Wedding decorations: invitations, place cards
Leather and Fabric
- Fashion: detailed cutouts on clothing and accessories
- Upholstery: custom patterns for furniture and car interiors
Each material fits certain applications, and knowing what works best can boost your project’s quality and efficiency. Laser cutting delivers precision and flexibility, making it ideal for a wide range of products in the U.S. market.
FAQs about Laser Cutting Materials
Can you laser cut glass with specialized cooling systems?
Cutting glass with lasers is tricky. It requires special cooling and slower speeds to avoid cracking or melting. While possible, it’s not common and usually done using specialized machines rather than standard CO2 or fiber lasers.
What’s the best laser for cutting metal?
Fiber lasers are your go-to for metals. They offer better precision and work great on stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and carbon steel. CO2 lasers can cut metals too but fiber lasers are preferred for speed and quality.
How do I know if a material is safe to laser cut?
Always check the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for chemicals and hazards. Also, consult your laser cutter’s manual or supplier for recommended materials. If it’s not listed, be cautious and run small tests with proper ventilation.
Why can’t PVC be laser cut?
PVC releases toxic chlorine gas when cut with a laser. This gas is harmful to your health and can corrode your machine. It’s best to avoid PVC and use alternatives like acrylic or polycarbonate instead.
How does HYCNC ensure safe laser cutting?
HYCNC uses advanced laser equipment with built-in safety features and expert operators. We carefully select materials and adjust settings for each job, ensuring safe, high-quality results every time. Plus, we emphasize ventilation and protective gear during processing to keep everyone safe.